Graphic content
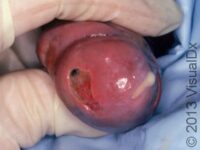
Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections that are passed from person to person by sexual activity. Although STDs are most often spread through vaginal, anal, or oral intercourse, skin-to-skin contact is enough to transmit many STDs.
STDs affect an enormous number of people throughout the world, regardless of age, sex, socioeconomic status, or ethnicity. Approximately 19 million new infections occur each year in the United States, and about half of these infections are in people aged 15-24. Roughly 50% of people in the United States will have at least one STD during their life.
People at higher risk for STDs are those who do not use condoms, have more than one partner, or have sex with people who have multiple partners, use intravenous drugs, and/or share needles. You can decrease your risk for getting an STD by using condoms every time you have sex (even during oral sex), limiting your number of sexual partners, or abstaining from sexual activity. If you think that you or your partner may have an STD, see your doctor as soon as possible. Early treatment can decrease your chance of spreading the infection and can prevent possible complications.
There are many types of STDs, and all have slightly different symptoms. STDs that cause prominent skin changes are discussed here. For example:
Important infections that are not discussed here include chlamydia, HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, and certain forms of gonorrhea, which you can learn more about by using the VisualDxHealth Trusted Search functionality in the menu bar.
Searching for pictures of genital warts or other STDs? Click any of the pictures of sexually transmitted diseases below to learn more.
References/Trusted Links:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs): Diseases & Related Conditions. http://www.cdc.gov/std/general/default.htm. Reviewed November 4, 2016. Accessed November 28, 2016.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs): CDC Fact Sheets. http://www.cdc.gov/std/healthcomm/fact_sheets.htm. Reviewed November 4, 2016. Accessed November 28, 2016.
Rosen T. Sexually transmitted diseases 2006: A dermatologist’s view. Cleve Clin J Med. 2006 Jun:73(6):537-, 542, 544-5.