Sunburn, First Aid
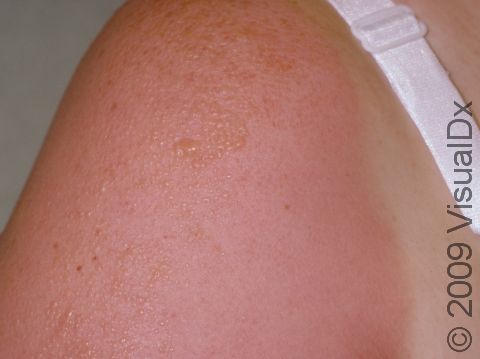
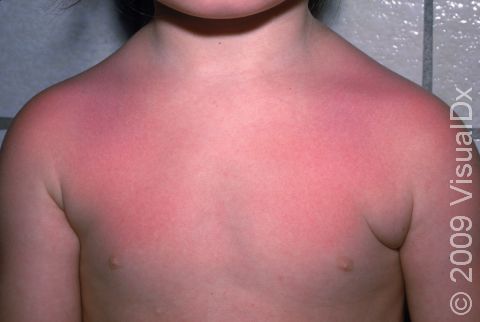
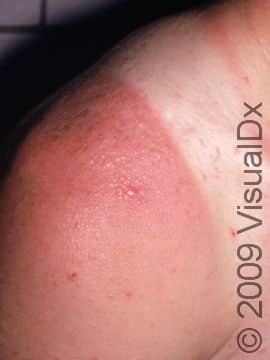
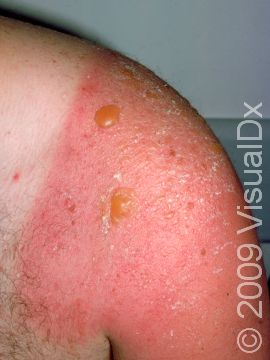
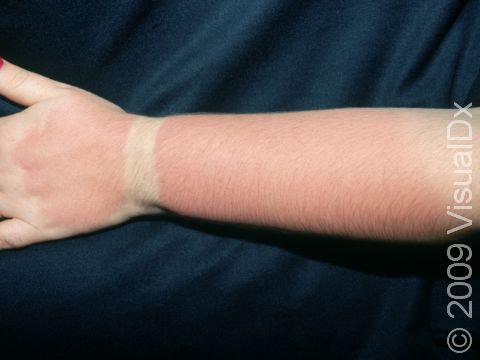
Sunburn is caused by the skin’s reaction to ultraviolet (UV) light exposure. It appears as reddening and tenderness of the skin and usually occurs within 4 hours after the UV exposure. Following sunburn, the skin may develop blisters or peeling of the outer layers of skin. Some oral medications used for other medical conditions, most commonly hydrochlorothiazide (a blood pressure medication), may make the skin more sensitive to sunburning.
Who's At Risk?
Sunburn can occur in almost anyone, particularly individuals with lighter skin colors.
Signs & Symptoms
Sunburn may occur on any sun-exposed area. Sunburn appears as redness within 4 hours following exposure, followed by deep redness and blister formation in severe situations. In darker skin colors, the redness may be harder to see. Long-lasting redness may be present for weeks after the actual burn.
Self-Care Guidelines
First Aid Guide
In the case of a sunburn:
- Avoid further direct sun exposure for at least a few days.
- Cool water or cool milk soaks may help cool and soothe the affected areas.
- Acetaminophen and ibuprofen can help decrease redness and pain associated with sunburn.
- Drink a lot of fluids.
- Avoid applying cream or ointment to the skin, as these make the pain worse by trapping the heat on the skin.
Do not attempt to break any blisters that may form; you can cover these with gauze if necessary. If blisters break on their own, apply a topical antibiotic ointment to help avoid infection. In the case of peeling skin, applying a moisturizer can help ease peeling and itch. Avoid topical products that end in “-caine” as they can sometimes further irritate the skin.
Prevention is very important. To reduce your risk of skin cancer later in life, sunburns should be prevented.
- Avoid direct sun in the middle of the day (10 AM to 3 PM). Snow and water reflect light to the skin, and clouds still let a lot of light through, so you are exposed to UV light even on cloudy days.
- Wear a hat with a wide brim in the sun. A baseball hat does not provide as much protection.
- Cover up with tightly woven clothing. Some manufacturers make specialty clothing with an ultraviolet protection factor (UPF) rating.
- When outdoors, wear a broad-spectrum sunscreen (one that protects against UVA and UVB rays) of at least sun protection factor (SPF) 30 on all exposed skin areas, including the lips. Apply to the skin generously 30 minutes before going outdoors, and reapply every 2 hours or after swimming or sweating a lot.
- Avoid using tanning beds.
Treatments
The medical professional may recommend:
- Acetaminophen and ibuprofen to help decrease the redness and relieve the discomfort.
- For severe reactions, prednisone, an oral steroid, may help reduce inflammation.
Visit Urgency
See your medical professional if there is severe discomfort and inflammation associated with sunburn or if you develop signs of infection (such as swelling, pus, or blisters that turn yellow or red).
Last modified on August 13th, 2024 at 10:30 am
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder