Explore Treatment Options for Eczema Relief
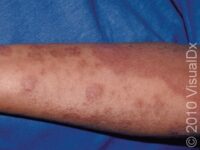
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a common skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. This chronic and relapsing skin disease is characterized by a rash and intense itch that can significantly impact one’s quality of life. In this article, we provide information on the various established and newer topical treatment options available for mild or localized eczema.
Preserving the Skin Barrier
Individuals with eczema have impaired skin barrier function, making it crucial to moisturize the skin to prevent eczema flares. Products containing skin moisturizing components such as ceramides (eg, CeraVe) and petroleum jelly (eg, Vaseline) are highly effective moisturizers, as they trap moisture in the skin and help reduce moisture loss. For optimal effectiveness, it is recommended to apply a thin layer of moisturizer onto slightly damp skin after showering and gently pat the skin dry.
Fighting Off Inflammation
An overactive immune system is another component to eczema, so topical anti-inflammatory agents are commonly recommended for mild or localized disease. Topical corticosteroids are among the most studied and utilized agents. One topical corticosteroid, hydrocortisone 1%, is a formulation that is commonly found over the counter. Topical corticosteroid formulations that require a prescription include desonide (eg, DesOwen), triamcinolone (eg, Kenalog), betamethasone (eg, Diprolene), fluocinonide (Vanos), and clobetasol (eg, Clobex). Side effects of topical steroids include skin thinning and skin color discoloration with prolonged use. To avoid thinning of the skin, do not use steroid creams for longer than 3 weeks continuously without a 1-week break in between. Topical steroids, used appropriately, are not significantly absorbed into the bloodstream.
Topical nonsteroidal calcineurin inhibitors were first approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for eczema in the early 2000s. There are currently 2 formulations: tacrolimus ointment (Protopic) and pimecrolimus cream (Elidel). Side effects include burning and itching that typically lasts for minutes for the first few days of treatment. Unlike topical steroids, these medications are not associated with thinning of the skin and can be used indefinitely as a treatment.
In recent years, 2 newer classes of anti-inflammatory topical nonsteroidal medications have been approved: crisaborole ointment (Eucrisa), which was approved by the FDA in 2016, and ruxolitinib cream (Opzelura), which was approved by the FDA in 2021.
Special Considerations
Several factors should be considered when deciding on the right topical formulation, including a person’s age, rash and itch severity, percentage of total body skin affected, location of affected skin, cost, and tolerability.
If you have eczema, it’s important to consult with a dermatologist to explore your treatment options and determine the most appropriate regimen for you.
Last modified on September 26th, 2023 at 2:19 pm