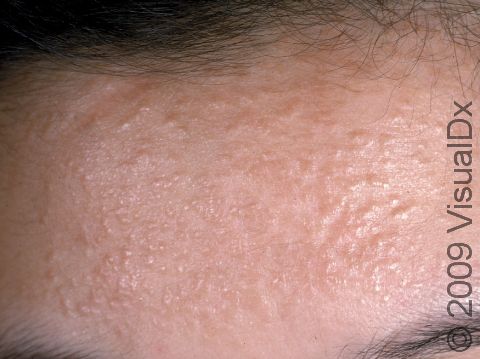
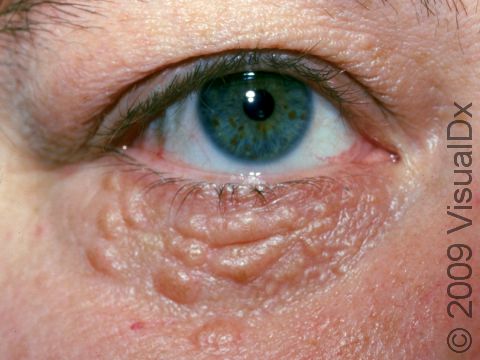
Syringoma
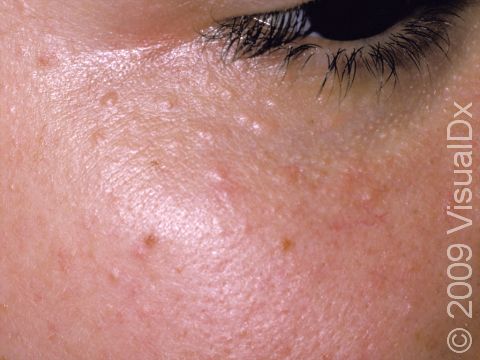
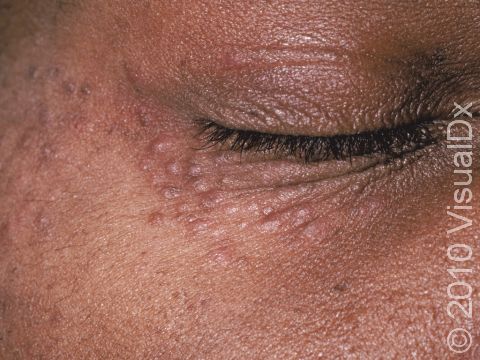
Syringomas are common tiny papules (small, solid bumps) usually found on the lower eyelids of young adults, but they can occur anywhere on the body and at any age. Syringomas are harmless and are caused by the overgrowth of cells from sweat glands (eccrine glands).
Who's At Risk?
Syringomas usually occur after puberty. Syringomas can develop in people of any race / ethnicity and sex, but females are more commonly affected.
Syringomas sometimes run in families. Up to 18% of people with Down syndrome have syringomas. People with diabetes are more likely to have a type known as clear cell syringoma.
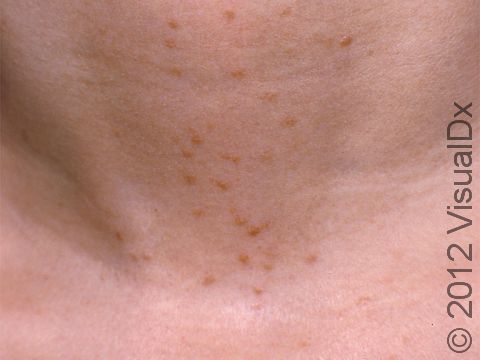
A less common type of syringoma called eruptive syringoma is more commonly seen in people with darker skin colors.
Signs & Symptoms
The most common locations for syringomas include the:
- Lower eyelids.
- Upper cheeks.
- Armpits.
- Chest.
- Abdomen.
- Forehead.
- Genitalia (penis or vulva).
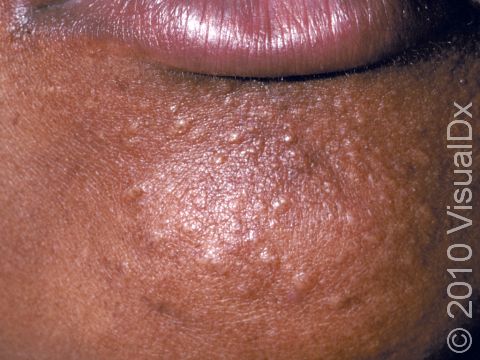
Syringomas typically appear as multiple small (1-3 mm), firm, skin-colored, yellowish, brown, or pink papules (small, solid bumps). They usually occur in clusters symmetrically on both sides of the body.
Eruptive syringomas may be tiny (usually 1-2 mm) and appear as multiple papules that all develop at the same time, usually on the chest and abdomen.
Syringomas do not itch or cause pain.
Self-Care Guidelines
No self-care is needed for syringomas.
Treatments
If the diagnosis is uncertain, your medical professional may want to perform a skin biopsy.
If diagnosed with syringomas, no treatment is necessary because they are harmless and there is no risk of syringomas becoming malignant. However, there are options to remove them if they are cosmetically bothersome. Note, however, there is the potential risk of scarring.
Removal of syringomas may include:
- Cutting out (excision) with a scalpel, scissors, or flexible razor blade.
- Burning with an electric needle (electrodessication).
- Laser treatment.
- Freezing (cryosurgery) with liquid nitrogen.
Visit Urgency
See a dermatologist or another medical professional if any new growth develops on your skin.
Trusted Links
References
Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
James WD, Elston D, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA. Andrew’s Diseases of the Skin. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019.
Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
Last modified on June 18th, 2024 at 2:37 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder