Fainting, First Aid
Fainting is a state of unconsciousness caused by decreased blood flow to the brain. It is usually quick and brief. Fainting is often due to low blood sugar or standing in one place for too long, but it can also be caused by a more serious medical matter.
Unlike when a person is asleep, someone who has fainted is not alert and not fully responsive to their surroundings. Because an unconscious person cannot cough, clear their throat, or turn their head if in distress, they are in danger of choking, making it very important to keep the airway clear while awaiting medical care.
Who's At Risk?
People with the following medical conditions are at an increased risk of fainting:
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- Anemia
- Any condition in which there is a rapid loss of blood, such as from internal bleeding
- Heart and circulatory problems
- Heatstroke or heat exhaustion
- Eating disorders (eg, anorexia and bulimia)
- Toxic shock syndrome
Additionally, those who stand in one place for a long time, particularly in high heat, are prone to fainting. Further, fainting can be caused by anxiety (eg, sudden stress or fright), severe pain, suddenly changing body position (eg, standing too quickly), and certain medications.
Signs & Symptoms
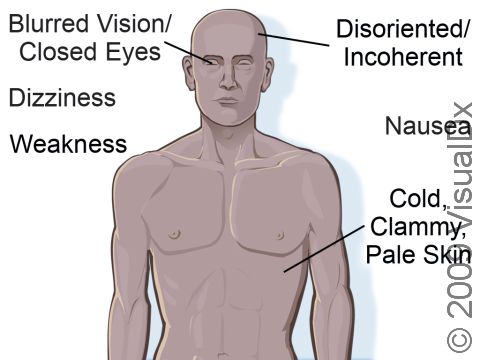
A person who faints often experiences dizziness, nausea, weakness, and/or blurred vision prior to losing consciousness, and they may have cold, clammy, pale skin. The person may be disoriented, incoherent, motionless, and silent.
Self-Care Guidelines
If you start to feel faint, it can be helpful to sit with your head between your knees or lie down.
First Aid Guide
In the event of another person fainting, attempt to:
- Prevent the person from hitting the ground.
- Lay the person down on the ground, face up, and elevate their feet 8-12 inches to help restore blood flow to the brain.
- Loosen any constrictive clothing.
- Apply a cool, wet compress to the person’s forehead.
- Discourage the person from standing until they have fully recovered.
Note:
- If the person vomits while they are unconscious or is bleeding from the mouth, quickly turn them on their side to allow the fluid to drain while protecting their airway.
- While the person is unconscious, do not attempt to give them anything by mouth.
If the person was injured while fainting, give first aid for any injuries (eg, bumps, bruises, or cuts). Bleeding should be stopped with direct pressure.
Treatments
If the person was injured during the fall, the medical professional will treat those injuries (eg, stopping bleeding, giving stitches).
As fainting can be caused by many underlying conditions, the medical professional may conduct tests to determine if there is an illness or injury in need of treatment.
Visit Urgency
If the person does not regain consciousness quickly (eg, within a couple minutes), is an older adult, is pregnant, or has a medical problem, call 911. While not typical, fainting can be a sign of serious illness, so seek treatment by a medical professional who can determine the cause and provide proper treatment.
Last modified on August 8th, 2024 at 4:43 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder