Beard Ringworm (Tinea Barbae)
Tinea barbae, commonly called beard ringworm or barber’s itch, is a fungal infection of the skin, hair, and hair follicles of the beard and mustache area. Beard ringworm may be passed on by direct contact with infected people or animals, with contaminated objects, or from the soil.
Although beard ringworm is most common in men, it may also affect women who have dark, coarse hair on their faces and necks.
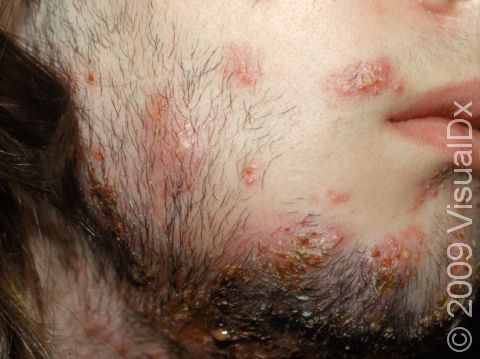
Sometimes severe cases of beard ringworm can result in a kerion, which appears as a thick, “boggy” or “mushy” nodule (a solid, raised bump that is firm to the touch) or plaque (a raised or bumpy area larger than a thumbnail) on the skin.
Who's At Risk?
Beard ringworm is seen almost exclusively in older teens and adult males.
Beard ringworm is more common in warm, humid climates. It is most frequently passed to humans from animals, so agricultural workers are the most commonly infected people with beard ringworm.
Signs & Symptoms
The most common locations for beard ringworm infection include the:
- Chin.
- Cheeks.
- Neck.
- Upper lip.
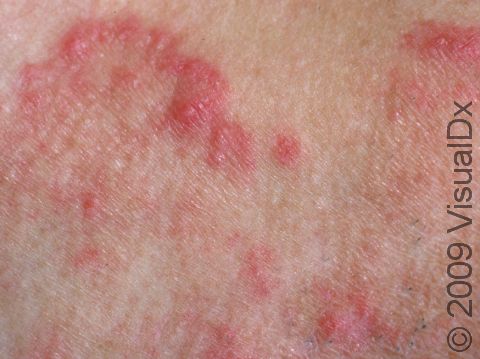
Beard ringworm may affect the outer surface of the skin and the hair follicles. It appears as a scaly plaque that may be small or large. In lighter skin colors, the border can be pink or red, whereas in darker skin colors, it can be dark red, purple, brown, or grayish. The central area may appear as normal skin; in other words, there is no skin color change in the center. Alternatively, small pustules (pus-filled bumps) may be seen around hair follicles in the affected skin. In the case of a kerion, you may see firm red nodules covered with pustules or scabs that may ooze blood and pus.
Beard ringworm is usually itchy. A kerion may be accompanied by fever and swollen lymph glands.
Self-Care Guidelines
It is extremely difficult to cure beard ringworm with only over-the-counter medications; it usually requires oral prescription medications. However, if the infection has just started, you can try an over-the-counter antifungal cream or lotion for up to 2 weeks, such as:
- Terbinafine.
- Clotrimazole.
- Miconazole.
Apply the cream to each lesion and to the skin 2 cm beyond the border of the affected area. Warm compresses can help drain pus and remove crusting on the lesions.
Stop shaving the affected area until you start treatment. Or if you must shave, use a new disposable razor each time you shave.
People often have tinea infections on more than one body part, so examine yourself for other ringworm infections, such as in the groin (tinea cruris, or jock itch), on the feet (tinea pedis, or athlete’s foot), and anywhere else on the body (tinea corporis).
Because ringworm is very contagious, avoid contact sports until lesions have been treated for at least 48 hours. Do not share towels, clothing, or other personal items with others until the lesions have cleared.
Have any household pets or farm animals evaluated by a veterinarian to make sure they do not have a fungal infection. If the veterinarian discovers an infection, be sure to have the animal(s) treated.
Treatments
To confirm the diagnosis of beard ringworm, your medical professional may scrape some surface skin material (scales) or pluck an affected hair and place it onto a glass slide for examination under a microscope. This procedure, called a KOH (potassium hydroxide) preparation, allows the medical professional to look for signs of a fungal infection.
If you have many pus-filled lesions or if deeper lesions are present, your medical professional may want to perform a fungal culture to determine the particular organism causing the infection.
Beard ringworm usually requires oral antifungal pills to get rid of the infection completely, so your medical professional will likely prescribe one of the following oral medications:
- Terbinafine
- Ultramicrosize griseofulvin
- Itraconazole
- Fluconazole
Beard ringworm should go away within 4-6 weeks after using effective treatment.
Visit Urgency
If the lesions do not improve after 1 or 2 weeks of applying over-the-counter antifungal creams, see your medical professional for an evaluation.
If the affected areas are deep and tender or if you have a fever or swollen lymph glands, see your medical professional as soon as possible.
References
Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
James WD, Elston D, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA. Andrew’s Diseases of the Skin. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019.
Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
Paller A, Mancini A. Paller and Mancini: Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology. 6th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022.
Last modified on June 17th, 2024 at 4:22 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder