Medication Overuse Headache
Medication overuse headache is a type of headache that affects people who regularly take pain relievers, such as to treat migraines, tension headaches, or other medical conditions. Medication overuse headache is defined as a headache occurring 15 or more days a month where headache medication has been overused (either taken too frequently or in too high a dose) for 3 or more months. These headaches are often worse than the headache the pain relievers were treating.
Unfortunately, quickly stopping the medication often causes severe “rebound headaches,” which continue the cycle of medication overuse. Treatment of medication overuse headache is best managed under the supervision of a medical professional.
Who's At Risk?
People with preexisting headaches (eg, tension headaches, migraines) and people who take pain medications for other medical conditions (eg, rheumatoid arthritis) are at risk of developing medication overuse headache. Medication overuse headache is more common in women than men.
Signs & Symptoms
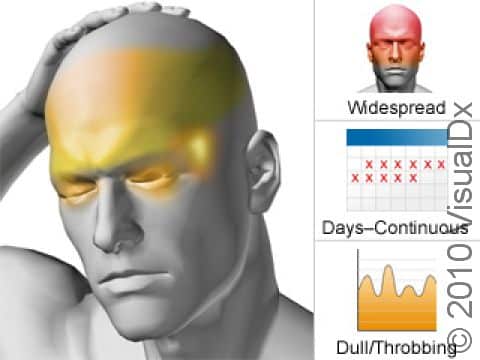
Medication overuse headache typically involves a dull, moderately intense, pressure-type feeling on both sides of the head, sometimes with the typical symptoms of migraine (eg, nausea, light and sound sensitivity). These headaches occur 15 or more days a month for 3 or more months. Medication overuse headaches most commonly occur in the morning.
Self-Care Guidelines
Although treatment of medication overuse headache is best managed under the supervision of a medical professional, there are self-care strategies that can be coupled with medical treatment:
- Eliminate caffeine and take a careful assessment of your diet and how it may be worsening your headaches, including keeping a headache diary and comparing the foods you have eaten with the days you had a headache.
- Conversation and support from others with medication overuse headache, such as in online forums like the NeuroTalk or BrainTalk communities can help. There are also groups and meetings organized by the American Headache Society.
- Yoga, exercise, massage therapy, and other relaxation techniques can also be beneficial.
Additionally, you should take headache treatments, including over-the-counter pain relievers, no more than 10 days per month.
Treatments
A combination of medicine and behavioral changes are usually necessary to effectively treat medication overuse headaches. The most important measure in treatment is stopping the overused medications under a medical professional’s care. It is also important to understand that the headaches typically get worse before they get better.
With the elimination of the overused medication and the associated worsening of headaches, certain medications may be used to “bridge” the time between stopping medications and successful relief.
Follow up with your medical professional regularly for treatment, and note that medication overuse headache may take weeks to months to treat. The occurrences of headaches and headache severity should start to improve in about 4-12 weeks; however, with discontinuation of the overused medication.
Visit Urgency
Seek medical care if your headaches become frequent and begin to interfere with your daily activities.
Call your medical professional for any headache if:
- You develop new symptoms not typical of prior headaches.
- An unusually severe headache occurs.
- You feel disoriented or lose consciousness.
- Your headache lasts an unusually long time.
- Your headache wakes you from sleep.
Immediately seek medical attention if you or someone you are caring for experiences:
- Stiff neck and a high fever with a headache.
- Loss of motor function (eg, your muscles don’t move normally), inability to think clearly, or convulsions with a headache.
- A head injury.
If you are currently undergoing treatment for medication overuse headache, contact your medical professional if you develop a new problem associated with a medication given to treat the headache, such as a rash or other side effects that negatively affect your life.
Last modified on October 7th, 2024 at 1:35 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder