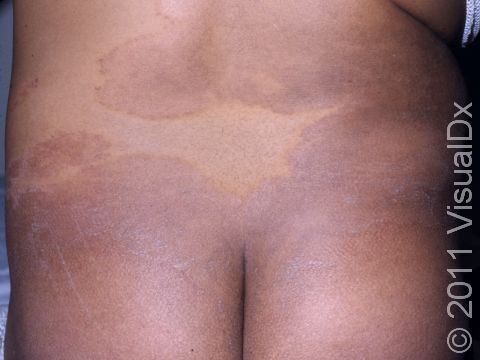
Ringworm (Tinea Corporis)
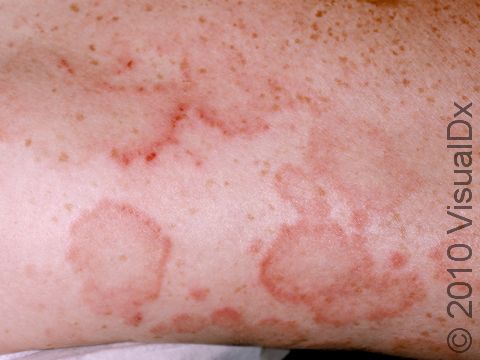
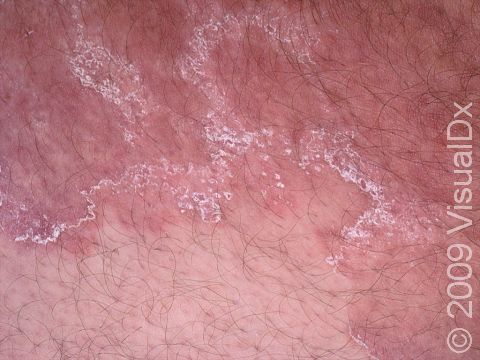
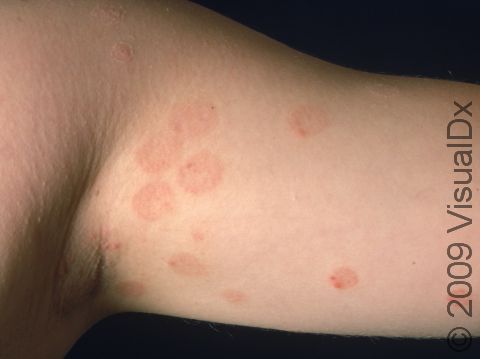
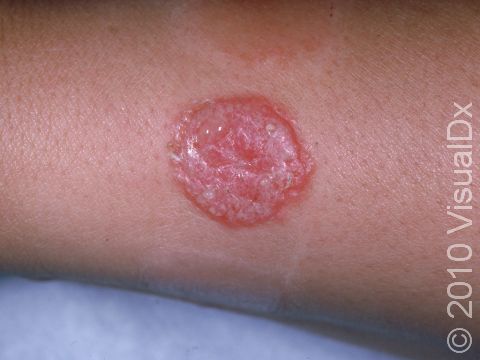
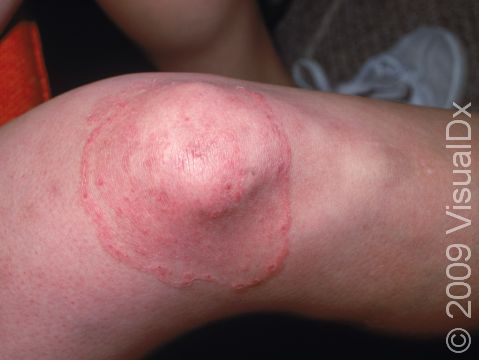
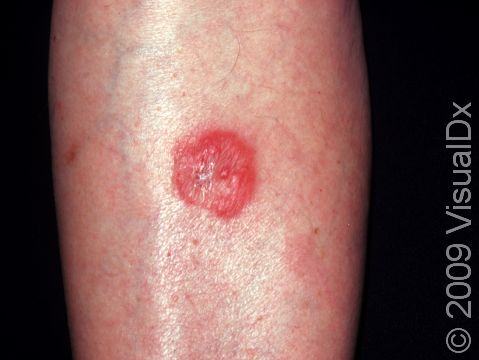
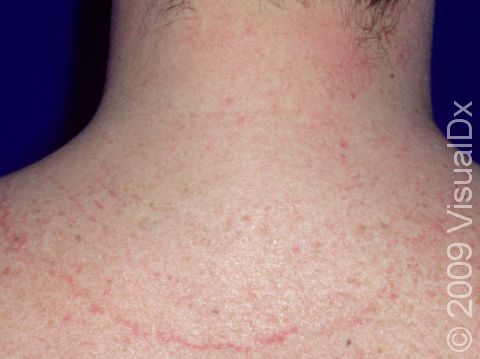
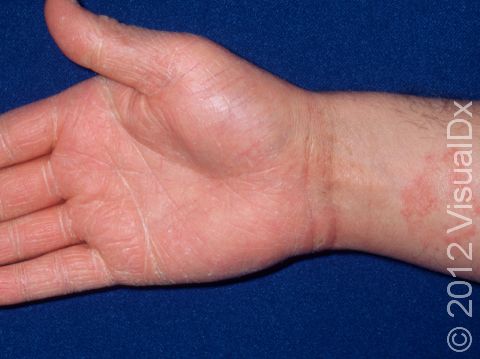
Tinea infections are commonly called ringworm because some may form a ring-like pattern on affected areas of the body. Tinea corporis, also known as ringworm of the body, tinea circinata, or simply ringworm, is a fungal infection on the surface of the skin. Ringworm may be passed to humans from direct contact with infected people, infected animals, contaminated objects (such as towels or locker room floors), and the soil.
There are several kinds of ringworm, including:
- The most common type, which appears as one or more rings on the skin. The edge of the ring is scaly or flaky.
- Majocchi granuloma, a deeper fungal infection of skin, hair, and hair follicles. It is most common in individuals who shave their legs.
- Tinea corporis gladiatorum, tinea corporis spread by skin-to-skin contact between wrestlers.
- Tinea imbricata, a form of tinea corporis seen in Central and South America, Asia, and the South Pacific.
Who's At Risk?
Ringworm may occur in people of all ages, races / ethnicities, and sexes.
People who are more likely to develop ringworm include:
- Children.
- Pregnant people who come into contact with infected children.
- People who have another tinea infection elsewhere on their bodies, such as tinea capitis (ringworm of the scalp), tinea faciei (ringworm of the face), tinea barbae (ringworm of the beard area), tinea cruris (ringworm of the groin, also called jock itch), tinea pedis (ringworm of the feet, also called athlete’s foot), or tinea unguium (ringworm of the fingernails or toenails).
- Athletes, especially those involved in contact sports.
- People in frequent contact with animals, especially cats, dogs, horses, and cattle.
- People with weakened immune systems.
- People who sweat heavily.
- People who live in warm, humid climates.
Signs & Symptoms
The most common locations for ringworm include the:
- Neck.
- Arms.
- Legs.
- Trunk (chest, abdomen, and back).
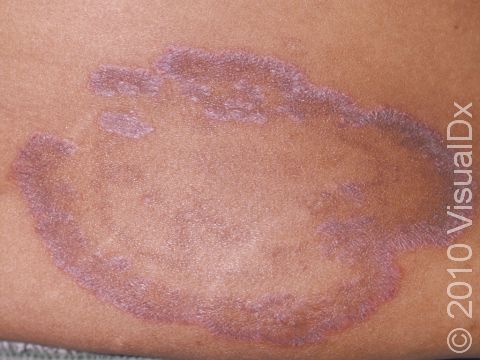
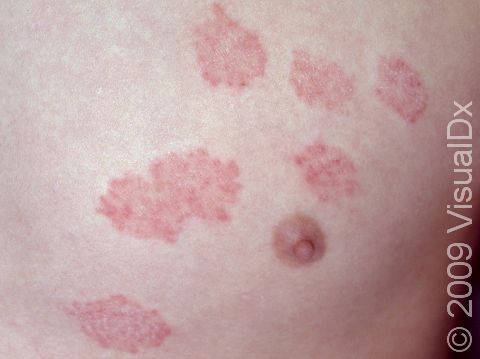
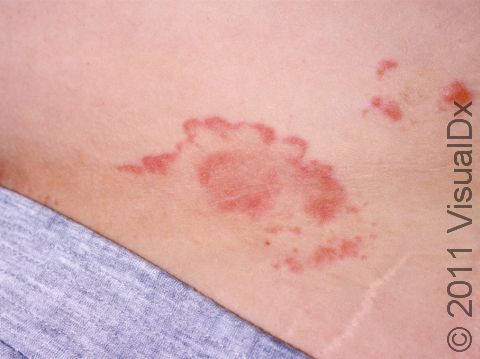
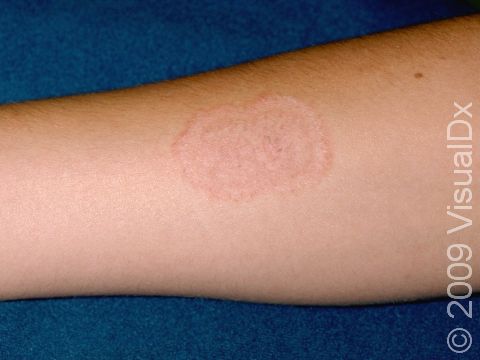
Ringworm appears as a ring-shaped plaque (a raised area of skin larger than a thumbnail) with a distinct scaly border. Lesions can range in size from 1 cm to 10 cm. In lighter skin colors, the lesion’s border can be pink or red, whereas in darker skin colors, it can be dark red, purple, brown, or grayish. The central area may appear as normal skin; in other words, there is no skin color change in the center. The border of the affected skin may contain papules (small firm bumps), vesicles (small fluid-filled blisters), or scabs.
Ringworm may cause itching or burning.
Self-Care Guidelines
If you suspect you have ringworm, you can try one of the following over-the-counter antifungal creams:
- Terbinafine (eg, Lamisil)
- Clotrimazole (eg, Lotrimin)
- Miconazole (eg, Micatin)
Apply the cream to each lesion and to the normal-appearing skin 2 cm beyond the border of the affected skin twice daily for at least 2 weeks, until the skin completely clears. Because ringworm is very contagious, avoid contact sports until lesions have been treated for at least 48 hours. Do not share towels, clothing, and other personal items with others until the lesions have cleared.
Because people often have tinea infections on more than one body part, examine yourself for other ringworm infections, such as on the face, beard area, groin, and feet.
Have any household pets evaluated by a veterinarian to make sure they do not have a fungal infection. If the veterinarian discovers an infection, be sure to have the animal treated.
Treatments
To confirm the diagnosis of ringworm, your medical professional may scrape some surface skin material (scales) onto a slide and examine them under a microscope. This procedure, called a KOH (potassium hydroxide) preparation, allows them to look for signs of a fungal infection.
Once the diagnosis of ringworm has been confirmed, you will likely be started on treatment with an antifungal medication. Most infections can be treated with prescription-strength topical creams and lotions, including:
- Econazole (Spectazole).
- Oxiconazole (Oxistat).
- Ciclopirox (eg, Loprox).
- Ketoconazole (eg, Nizoral).
- Naftifine (Naftin).
- Butenafine (Lotrimin, Mentax).
- Luliconazole (Luzu).
Rarely, more extensive infections or those not improving with topical antifungal medications may require 3-4 weeks of treatment with oral antifungal pills, including:
- Terbinafine (Lamisil).
- Itraconazole (Sporanox).
- Fluconazole (Diflucan).
The ringworm should go away within 4-6 weeks after using effective treatment.
Visit Urgency
If large areas of the body are affected or if the lesions do not improve after 1-2 weeks of applying an over-the-counter antifungal cream, see a medical professional for evaluation.
References
Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
James WD, Elston D, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA. Andrew’s Diseases of the Skin. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019.
Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
Paller A, Mancini A. Paller and Mancini: Hurwitz Clinical Pediatric Dermatology. 6th ed. St. Louis, MO: Elsevier; 2022.
Last modified on June 14th, 2024 at 9:34 am
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder