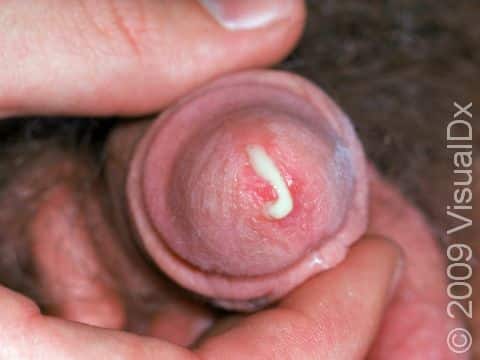
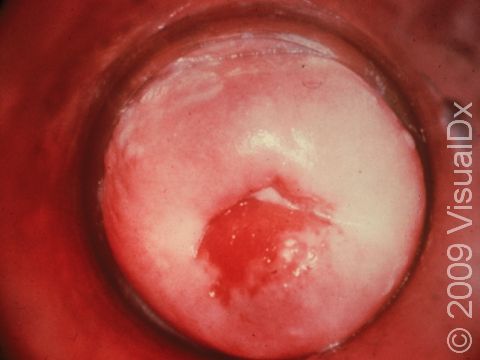
Gonorrhea, Primary Infection
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by the bacterium Neisseria gonorrhea. It is a contagious infection spread by unprotected oral, vaginal, or anal sex with an infected partner. The bacterium can live in the mouth, semen, or vaginal fluids of infected persons. It is possible to be infected and not have symptoms but still spread the infection to others.
If the infection is not treated, it can spread to other parts of the body, including the throat, joints, and eyes (potentially leading to blindness). Complications from gonorrhea infection include pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can affect fertility in women; inflammation of the testicles (epididymitis), which can lead to infertility in men; blindness in an infant infected during delivery; and widespread infection with a fever, rash, and joint pain.
Who's At Risk?
Anyone who is sexually active is at risk for gonorrhea as well as other STIs. People aged 15-24 years are at the highest risk for contracting gonorrhea. In the United States, 75% of cases occur in those younger than 30 years. Further risk factors for gonorrhea infection include having a new sexual partner, having more than one sexual partner, having a sexual partner who has other sexual partners, previous history of other STIs, inconsistent condom use, and substance abuse.
There is no immunity developed from infection with gonorrhea, so the infection can be acquired again if there is sexual contact with an infected person.
Signs & Symptoms
Individuals with gonorrhea may have mild or no symptoms, particularly women.
Typically the time between infection to symptom onset is 2-7 days. Symptoms often start with only mild discomfort with urination. Later, there may be:
- Frequent and painful urination or defecation.
- A thick, yellow discharge from the penis, or vaginal discharge and vaginal bleeding between periods.
- Pelvic pain if the infection has spread higher up the female genital tract.
- Bloody discharge from the rectum.
- Pain with sexual intercourse.
- A sore throat if throat infection is present.
Occasionally, the infection can spread throughout the body and presents with symptoms of fever, chills, swollen or painful joints, and small pustules (pus-filled lesions) that may be red or purple on the hands or feet. This is referred to as the arthritis-dermatitis syndrome.
Self-Care Guidelines
Gonorrhea is highly contagious and can have many serious side effects if left untreated. If you are sexually active and have symptoms of gonorrhea or may have been exposed to gonorrhea, you should seek medical care immediately. You should avoid any further sexual activity and notify any previous sexual partners.
Gonorrhea can be prevented by using condoms correctly during any sexual contact.
Treatments
Your medical professional will take a sample of bodily fluid to be cultured in a lab. Tests may also be done to check for other STIs that commonly occur at the same time as gonorrhea.
Antibiotics are prescribed for treatment of gonorrhea or suspected gonorrhea. Because drug-resistant strains of bacteria are becoming common, it is extremely important that you finish all the antibiotics prescribed to you and go back to your medical professional if your symptoms persist or come back following treatment.
Your sexual partner or partners also will also require a medical examination, testing, and treatment if gonorrhea is found.
Visit Urgency
See a medical professional and abstain from sexual contact if:
- There is a discharge or bleeding from the vagina, penis, or rectum.
- There is pelvic pain.
- There is burning or pain during urination or defecation.
- You are concerned that or know that your sexual partner has symptoms of gonorrhea or has been diagnosed with gonorrhea.
References
Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Gonorrhea – CDC basic fact sheet. CDC. https://www.cdc.gov/std/gonorrhea/stdfact-gonorrhea.htm. Updated 2022 August 22.
James WD, Elston D, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA. Andrew’s Diseases of the Skin. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019.
Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
Last modified on June 17th, 2024 at 2:42 pm
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder