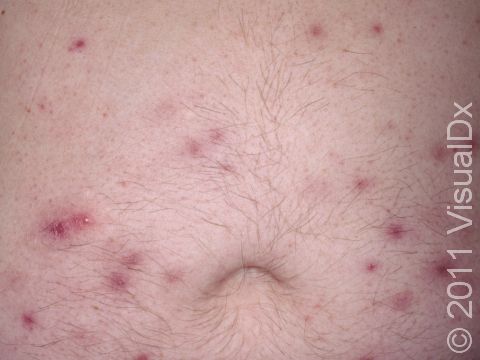
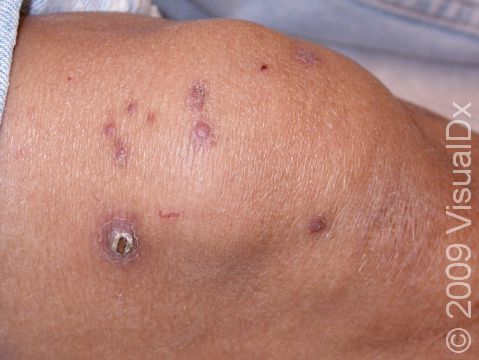
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a skin condition caused by an inflammation of one or more hair follicles. It typically occurs in areas of irritation, such as sites of shaving, skin friction, or rubbing from clothes. In most cases of folliculitis, the inflamed follicles are infected with bacteria, especially with Staphylococcus (or “staph”) organisms, that normally live on the skin. Bacteria such as Pseudomonas may live in hot tubs, spas, and swimming pools and may also cause folliculitis.
Who's At Risk?
Folliculitis occurs in people of all ages, races / ethnicities, and sexes.
Further risk factors for folliculitis include:
Signs & Symptoms
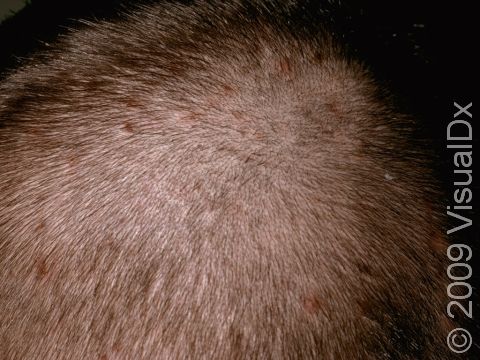
The most common locations for folliculitis include the:
- Scalp.
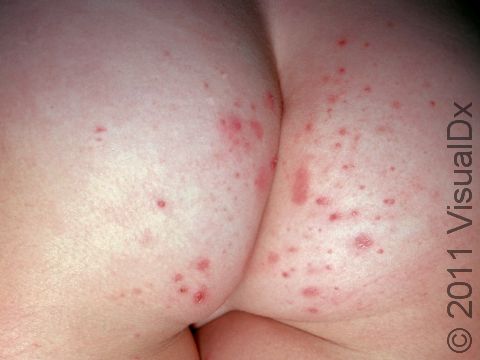
- Buttocks.
- Thighs.
- Areas that are shaved, such as the beard area, underarms, groin, and legs.
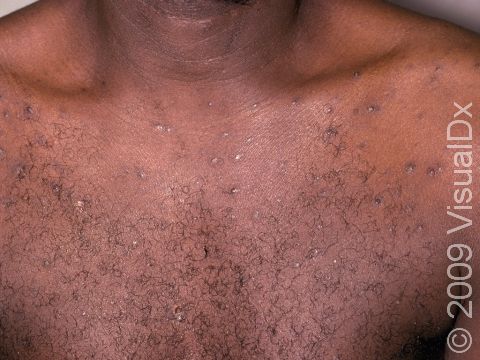
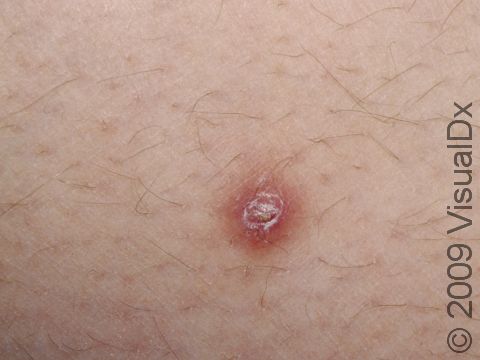
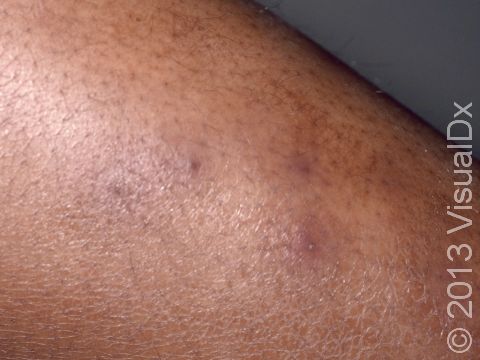
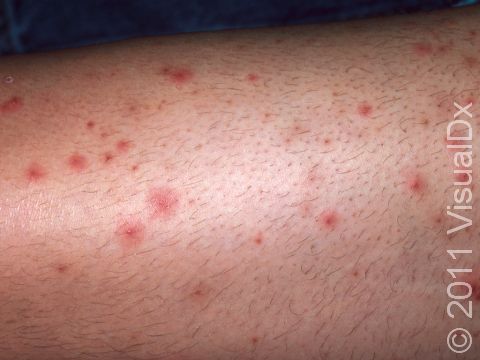
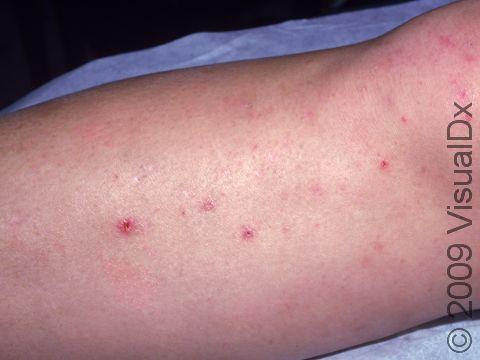
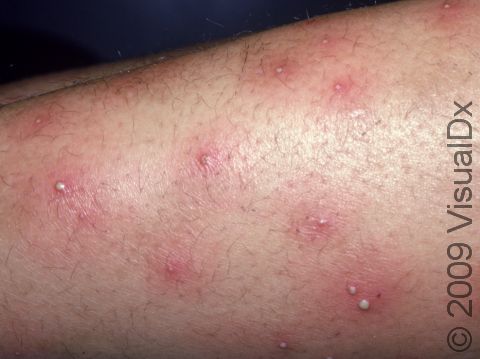
Individual lesions of folliculitis include pustules (pus-filled bumps) and papules (small solid bumps) centered on hair follicles. These pustules and papules may be pierced by an ingrown hair, can vary in size from 2-5 mm, and are often surrounded by a ring of inflamed skin. In lighter skin colors, the lesions may be any shade of pink or red. In darker skin colors, the redness may be harder to see, and the bumps may be the only sign of the folliculitis. Occasionally, a folliculitis lesion can break open, drain, and then form a scab on the surface of the skin.
Mild and moderate cases of folliculitis are often tender and itchy. More severe cases of folliculitis, which may be deeper and may affect the entire hair follicle, can be painful.
Mild and moderate cases of folliculitis usually clear up quickly with treatment and leave no scars. More severe cases of folliculitis may lead to complications such as cellulitis (an infection of the deeper skin tissue), scarring, and permanent hair loss in the affected area.
Self-Care Guidelines
To prevent folliculitis:
- Shave in the same direction of hair growth.
- Avoid shaving irritated skin.
- Use an electric razor or a new disposable razor each time you shave.
- Avoid tight, constrictive clothing, especially during exercise.
- Wash athletic wear after each use.
- Consider other methods of hair removal, such as depilatories.
The following may help to clear up folliculitis if it is mild:
- Use an antibacterial soap or wash (eg, PanOxyl Acne Creamy Wash, Hibiclens).
- Launder towels, washcloths, and bed linens frequently, and do not share such personal items with others.
- Wear loose-fitting clothing.
Treatments
Folliculitis is fairly easy to diagnose in most cases. Your medical professional may perform a bacterial culture to determine the cause of the folliculitis and may recommend:
- Antibacterial wash, such as chlorhexidine (eg, Betasept, Hibiclens).
- Topical antibiotic lotion or gel, such as erythromycin (eg, AkneMycin) or clindamycin (eg, Cleocin T).
- Oral antibiotic pills, such as cephalexin (eg, Keflex) or doxycycline (eg, Vibramycin, Monodox), or ciprofloxacin (eg, Cipro) in the case of hot tub folliculitis.
Occasionally, the bacteria causing the infection are resistant to treatment with the usual antibiotics. This can sometimes cause a more severe form of folliculitis. Depending on the circumstances, your medical professional may consider more aggressive treatment that includes prescribing:
- A combination of two different oral antibiotics, including trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (eg, Bactrim), clindamycin (eg, Cleocin), amoxicillin (eg, Amoxil), linezolid (eg, Zyvox), or tetracycline.
If your medical professional prescribes antibiotics, be sure to take the full course of treatment to avoid allowing the bacteria to develop resistance to the antibiotic prescribed.
Visit Urgency
Make an appointment to be evaluated by a dermatologist or another medical professional if the above self-care measures do not resolve the condition within 2-3 days, if symptoms come back frequently, or if the infection spreads.
Be sure to tell the medical professional about any recent exposure to hot tubs, spas, and swimming pools, as a less common form of folliculitis may be caused by contamination from these water sources.
If you are currently being treated for a skin infection that has not improved after 2-3 days of antibiotics, return to your medical professional.
References
Bolognia J, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L. Dermatology. 4th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018.
James WD, Elston D, Treat JR, Rosenbach MA. Andrew’s Diseases of the Skin. 13th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2019.
Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology. 9th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education; 2019.
Last modified on June 14th, 2024 at 9:05 am
Not sure what to look for?
Try our new Rash and Skin Condition Finder